Ketones in Urine: What It Means and When to See a Doctor

TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What Are Ketones and Why Do They Appear in Urine?
- Common Causes of Ketones in Urine
- Ketones in Urine and Diabetes: The Critical Link
- Other Health Conditions That Can Cause Ketones in Urine
- Symptoms That Indicate High Ketone Levels
- How Ketones in Urine Are Diagnosed
- Possible Complications of High Ketone Levels
- Treatment Options for Managing Ketones in Urine
- Prevention Tips to Maintain Healthy Ketone Levels
- When to See a Doctor for Ketones in Urine
- Conclusion
- FAQs
The presence of ketones in urine shows that your body has switched to burning fat instead of its preferred fuel source, glucose. A urine ketone test detects these substances that form during this alternative metabolic process. Your body can safely handle small traces of ketones, but moderate to large amounts might signal a serious health issue.
High ketone levels, or ketonuria, can result from many factors including diet changes and health conditions. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) remains the most serious condition tied to high ketone levels. This dangerous state happens when your body's blood becomes too acidic from high levels of blood acids and you need immediate medical care.
The signs of ketonuria include increased thirst, frequent urination, unusual tiredness, nausea, vomiting & breath that smells like fruit or acetone. Early detection of ketones through regular testing is vital if you have diabetes (as it allows treatment before the condition worsens). Knowledge about normal and dangerous ketone levels helps you decide when to seek medical help.
What Are Ketones and Why Do They Appear in Urine?
Your body uses ketones as backup fuel when glucose isn't readily available. We create ketones at the time of fasting, intense exercise, or when insulin levels are low. Ketone bodies are water soluble molecules that do not bind to plasma proteins. They filter through the kidneys easily (only shows up in urine once blood levels reach 0.1 to 0.2 mM).
Common Causes of Ketones in Urine
These factors can trigger ketonuria:
Long periods without food or starvation
Low-carbohydrate or ketogenic diets
Intense physical activity
Pregnancy, especially the third trimester
Ketones in Urine and Diabetes: The Critical Link
Ketones signal potentially dangerous conditions for people with diabetes (especially type 1). Cells cannot use glucose without insulin, which forces the body to break down fat. This process can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). The ketone body ratio may jump from normal (1:1) to as high as 10:1. DKA becomes life-threatening without treatment.
Other Health Conditions That Can Cause Ketones in Urine
Ketonuria can result from:
Alcohol use disorder (alcoholic ketoacidosis)
Eating disorders
Severe vomiting or diarrhoea
Certain digestive diseases
Medication effects (corticosteroids, diuretics)
Symptoms That Indicate High Ketone Levels
The warning signs are:
Excessive thirst
Frequent urination
Headaches
Nausea
Abdominal pain
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Fruity-smelling breath (appears as ketone levels increase)
Confusion (in severe cases)
How Ketones in Urine Are Diagnosed
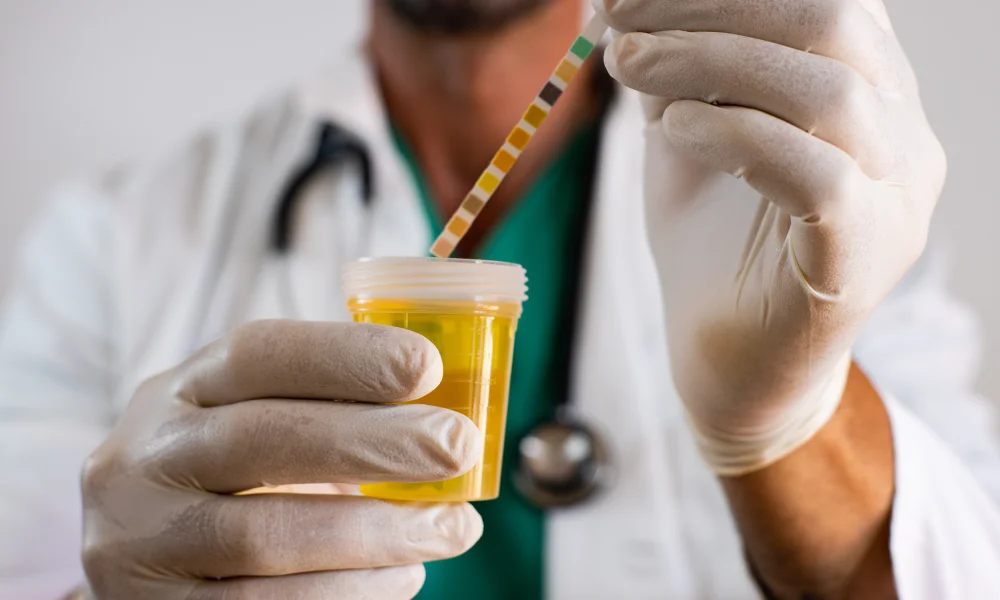
Doctors use special dipsticks that change colour when they detect ketones in urine. The results appear as negative, trace, small (less than 20 mg/dL), moderate (30-40 mg/dL), or large (above 80 mg/dL). Blood tests offer more precise ketone measurements, with normal levels staying below 0.6 mmol/L. You can perform these tests at home or get them done at medical facilities.
Possible Complications of High Ketone Levels
If left untreated high ketone levels can progress to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA triggers serious complications. They are:
Cerebral oedema
Hypoglycemia
Low potassium levels
Kidney failure
Shock
Pulmonary oedema.
Without proper medical intervention, DKA can lead to coma or death.
Treatment Options for Managing Ketones in Urine
The treatment approach depends on the mechanisms:
For diabetes: insulin therapy and IV fluids
For dehydration: increased fluid intake
For dietary causes: adjusting carbohydrate intake
For illness: treating underlying conditions
Prevention Tips to Maintain Healthy Ketone Levels
You can maintain healthy ketone levels by:
Monitoring blood sugar regularly
Taking prescribed medications consistently
Staying properly hydrated
Following a balanced diet
When to See a Doctor for Ketones in Urine
Medical attention becomes necessary immediately if you experience:
Moderate/large ketone levels
Blood sugar above 240 mg/dL
Persistent vomiting
Difficulty breathing
Abdominal pain
Extreme thirst
Fruity-smelling breath
Conclusion
Ketone knowledge plays a vital role in metabolic health management. These compounds appear normally during fasting or low-carb diets, but they definitely need attention when they show up unexpectedly or reach high levels.
Your body makes small amounts of ketones naturally, but higher quantities often indicate an underlying problem. Most cases of ketonuria respond well to proper treatment through insulin therapy, increased fluid intake, or dietary changes. This straightforward strategy provides peace of mind and protects your overall health.
FAQs
What does it mean when ketones are present in urine?
Ketones in urine mean your body is burning more fat than glucose for energy. Normal levels (less than 20 mg/dL) should not worry you. However moderate or high levels might point to a severe metabolic imbalance.
Can dehydration cause ketones in urine?
Your urine becomes concentrated due to dehydration, which might lead to ketones because glucose becomes less available & fat breakdown starts. Good hydration helps keep ketone levels normal.
Are ketones in urine always a sign of diabetes?
Ketones don't always mean you have diabetes. They can appear from low-carb diets, fasting, too much exercise, pregnancy, or illness. You should still see a doctor if moderate-to-high ketone levels appear without explanation.
What are the symptoms of high ketone levels?
You might notice extreme thirst, frequent bathroom trips, and tiredness first. Higher levels can cause nausea, vomiting, stomach pain, breath that smells like fruit, and quick breathing.
How are ketones in urine detected and monitored?
Diagnostic tests:
Urine test strips - show different colours based on ketone levels
Blood ketone metres - give exact measurements.
Can diet changes help reduce ketones in urine?
People on low-carb diets can reduce their ketone levels by eating more carbohydrates. Diabetic patients need to follow their prescribed meal plans and take insulin correctly.
What is diabetic ketoacidosis and how is it related to ketones?
Your blood becomes dangerously acidic with DKA because a lack of insulin leads to too many ketones. This life threatening condition can develop in just 24 hours.
When should I seek medical help for ketones in urine?
Rush to get medical care if:
Your diabetes comes with ketone levels above lower levels
Blood sugar readings go beyond 240 mg/dL






