Endometrium Cancer: Know About The Symptoms And Treatment of Uterine Cancer
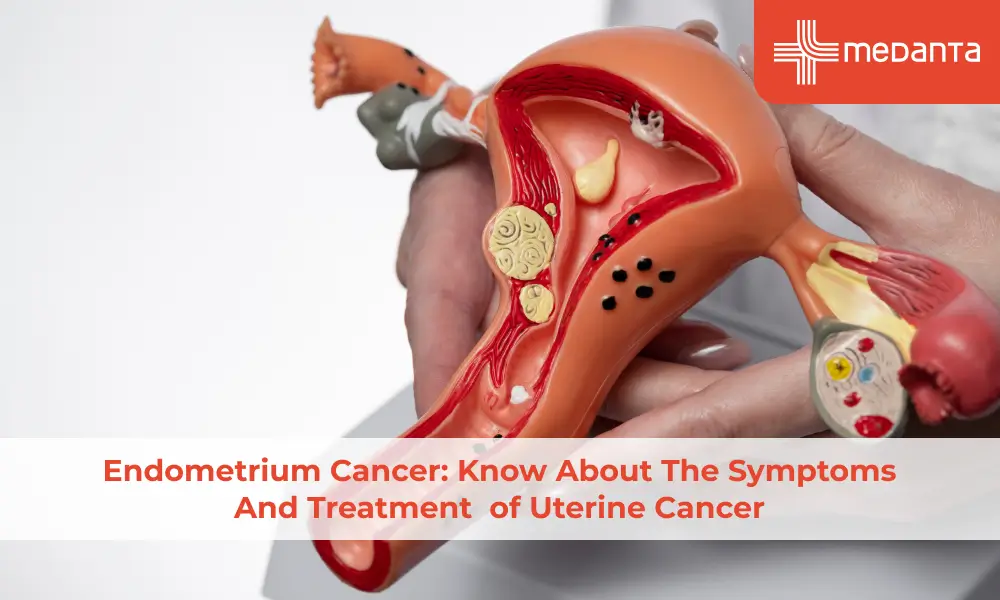
The uterus is a hollow, pear-shaped organ present in the female pelvic cavity. The top of the uterus is known as the fundus, the middle is the corpus, and the bottom is the cervix; the inner wall of the uterus is the endometrium, and the outer layer is the myometrium.
The above diagram represents the female pelvic cavity, also known as the uterus
What Is Uterine Cancer?
It is the most common type of cancer of the female reproductive system. Most uterine cancers are caused due to the abnormal or malignant growth of cells that comprise the endometrial tissue. Malignant means that it can spread and destroy tissue in organs that are in the vicinity, such as the bladder, rectum, vagina, fallopian tubes and ovaries. It can also metastasize to more distant organs. Fortunately, endometrial cancer grows very slowly and can be detected before progressing to severe levels with regular checkups and proper diagnoses.
Who Is at Risk of Uterine Cancer?
Women who are past menopause are at a higher risk for uterine cancer and it is more prevalent in women who are above the age of 40. You could be at a high risk for uterine cancer if you:
Got your period early
Are overweight or obese
Suffer from diabetes or high blood pressure
Have few or no children
Have a history of infertility, irregular periods, or abnormal cell growth in the uterus
Have a family history of endometrial, colorectal, or breast cancer
Take drugs like tamoxifen or estrogen-only hormone replacement
Regularly consume high-fats like red meat
What Are The Symptoms of Uterine Cancer?
In many cases, uterine cancer can go unnoticed since it doesn’t show any obvious symptoms. However, it does have some clear giveaways such as:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding (most common symptom)
Weird and frequent vaginal discharge
Pain during urination and sex
Recurrent pelvic pains
How Is Uterine Cancer Diagnosed?
While a pelvic exam can detect any abnormal growth in the uterine and vaginal cavity, your doctor may also ask you to undergo a PAP (Papanicolaou test), an ultrasound or a biopsy. Occasionally, a CT scan or MRI may also be done in order to help confirm the diagnosis. Any cancer between stages 0 to IV can be determined by a biopsy, chest X-ray, and/or CT or MRI scans.
How Is Uterine Cancer Treated?
Your treatment options depend on the progression of uterine cancer, age, and general health. Depending on these factors the doctor will recommend a combination of the following: surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy. Your doctors can then decide what treatment plan is best for you on the basis of the extent and aggression of the cancer cells.
Surgical therapy may involve the removal of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, the adjacent lymph nodules and a portion of the vagina. This is decided by doctors on a case by case basis.
Radiation therapy may include external or internal radiation depending on the severity of cancer.
Chemotherapy usually involves IV administration of drugs designed to destroy the malignant cells. This will be done via repeated cycles of drug administration, followed by a rest period.
Hormone therapy usually includes doses of progesterone, used on the uterine cancer cells that require estrogen for growth.
What Else Do I Need to Know?
It is always a good idea to get a second opinion from the referrals made by your doctor to specialists.
Follow-up care is crucial when it comes to recovery. With regular follow-ups, complications can be treated early, and possible cancer recurrence can be diagnosed early.






