Deep Brain Stimulation or the Brain Pacemaker Surgery
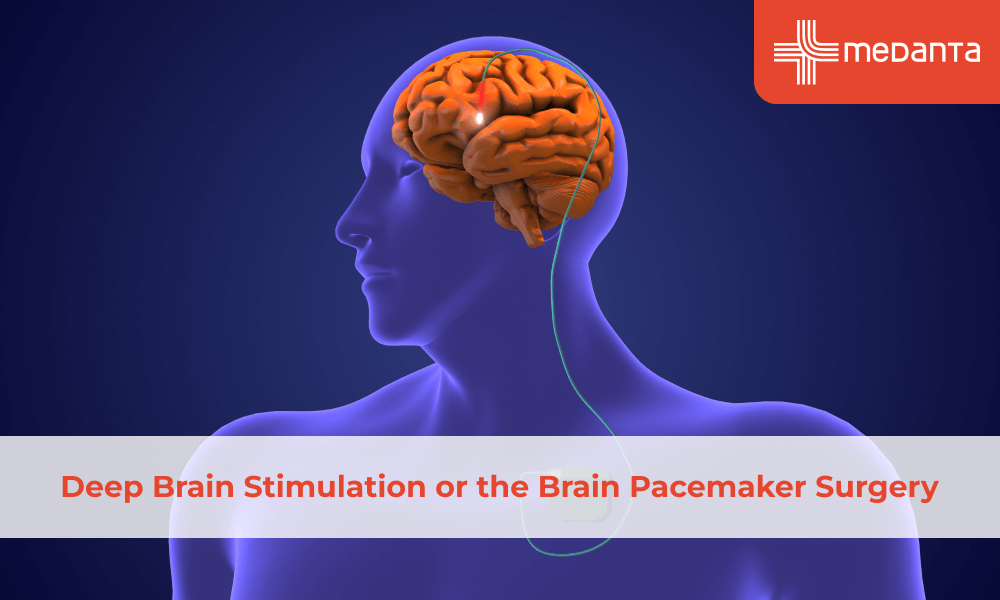
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Brain pacemaker surgery known as Deep Brain Stimulation or DBS, stands as a major step forward to treat complex neurological conditions. This procedure brings new possibilities to people with chronic neurological issues who stay impaired even after taking medicines. Dr. Anirban Deep Banerjee from Medanta Gurugram explains that this method works like a heart pacemaker. Instead of connecting wires to the heart, surgeons place them in precise spots in the brain and link them to a pulse generator or what they call a "pacemaker."
Understanding Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation requires a surgery where doctors place electrodes in specific parts of the brain. These electrodes link to a pulse generator similar to a pacemaker, which sits under the skin near the chest. This device sends electrical pulses to certain brain areas to adjust unusual brain activity and ease neurological issues.
This technology is unique. It continuously sends electrical signals to your brain's problem area. This helps improve life for patients by addressing symptoms that medicine alone has not fixed.
Conditions Approved for Deep Brain Stimulation
Dr. Banerjee states that there are recognised conditions to treat with deep brain stimulation:
Movement Problems: Doctors most often recommend DBS to treat movement issues. These include, but are not limited to, Parkinson's disease, tremors, essential tremor, and dystonia.
Epilepsy: Doctors also use DBS to manage severe epilepsy. These patients show no benefits with regular treatments.
Mental Health Conditions: Sometimes, DBS can treat certain mental health issues like OCD. This happens when other treatments fail.
Doctors turn to DBS when a condition worsens to the point where medicines stop working well or cause serious problems.
How DBS is Done: A Team Effort
Deep Brain Stimulation needs a team with experts from different medical fields. Dr. Banerjee shares that the team includes:
A functional neurosurgeon
A neurologist focused on movement disorders
A neurophysician
A neuropsychiatrist
The process starts with checking the patient at a movement disorder clinic to see if they qualify for the surgery. If they are eligible, they go through a detailed MRI scan that is made for DBS.
How the Surgery Works
Doctors perform DBS surgery in two parts:
Part One
Before the surgery starts, doctors attach a stereotactic head frame to the patient’s head. Dr. Banerjee explains that this frame works like a car’s GPS by giving precise directions to locate tiny brain areas, sometimes just a few millimetres wide.
Using the stereotactic frame, surgeons plan through a computer system and then place two wires in the brain, one on each side. Patients stay awake during this part of the operation. This lets the team observe the therapy’s effects and tweak things if needed.
Stage Two
In the second part, the wires already implanted get connected to a pulse generator, which acts as a pacemaker. This step is done under general anaesthesia.
Advantages of Deep Brain Stimulation
Dr. Banerjee highlights that DBS provides a lasting option to help patients dealing with advanced neurological problems. A major benefit of this method is its ability to be adjusted and undone if needed. Your doctor can fine-tune your device over time. This procedure is called "brain pacemaker programming". It matches the progression of the condition in your body.
Conclusion
Deep Brain Stimulation marks a major step forward in neurosurgery. It gives hope to those battling severe neurological diseases where other treatments have failed. Dr. Banerjee points out that this innovative approach brings a reversible and adaptable long-term answer improving life for people struggling with tough neurological challenges.
FAQs
What is Deep Brain Stimulation?
Deep Brain Stimulation is a type of surgery. Your doctor places electrodes in the brain. They link them to a pulse generator. This pulse generator works like a pacemaker. It sends out steady electrical signals to manage unusual activity in your brain and lessen symptoms linked to some brain conditions.
What can Deep Brain Stimulation treat?
Doctors use DBS to help with movement problems like Parkinson's disease, dystonia, and essential tremor. It is also approved to treat hard-to-manage epilepsy in adults and some mental health conditions like Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.
When do doctors choose Deep Brain Stimulation?
Doctors consider DBS when neurological disorders progress to a point where medicines no longer work well or cause serious side effects that are hard to manage.
Do patients stay awake during Deep Brain Stimulation surgery?
Most of the time yes. Patients stay awake during the first part of the surgery when doctors place electrodes in the brain. This helps the surgical team check how well the stimulation works right away. The second part where they put the pulse generator in the body, is done with the patient under general anaesthesia.
Can patients control the stimulation themselves?
Certain DBS systems give patients some ability to tweak their stimulation settings, but within limits set by their doctor. Most changes still happen during professional programming appointments.
Can Deep Brain Stimulation be undone?
Yes, DBS offers the benefit of being undoable. Doctors can stop the stimulation, and if needed, they can take out the system. However, removing it would involve another surgery.






