-
Steps to take before the procedure
Your doctor will thoroughly prepare you for the treatment. You might be given blood thinner to avoid blood clotting and some other medications that will help you relax. Discuss with your doctor about the changes you have to make in your lifestyle and the medicines that you need to take or avoid.

-
What happens during the procedure?
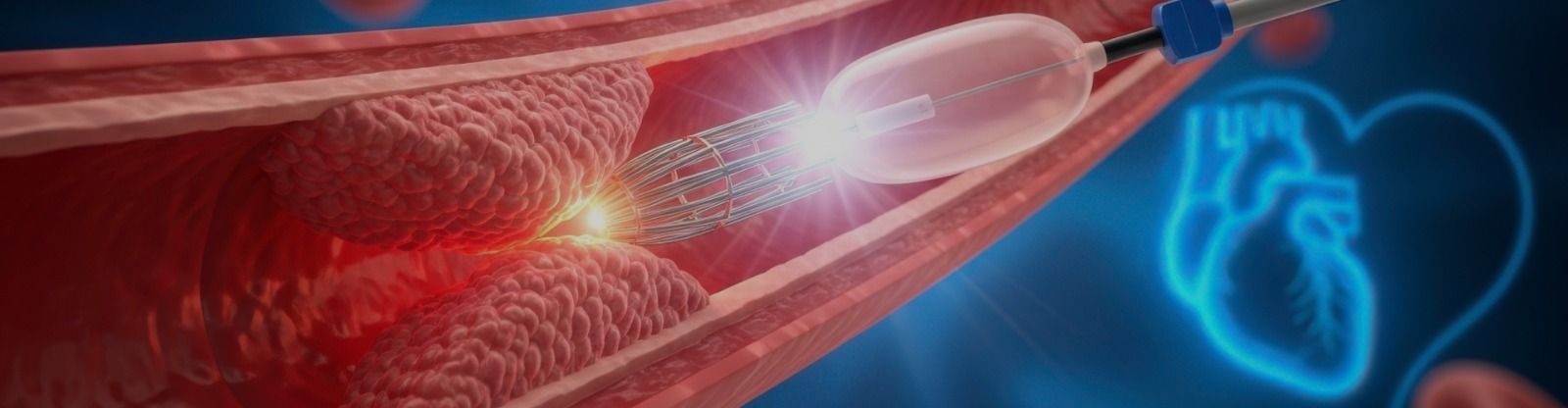
The procedure is performed in a cardiovascular catheterization laboratory, under local anesthesia. The surgery is often done in conjunction with balloon angioplasty. The cardiovascular surgeon inserts a stent (a thin tube-like structure with a balloon at the end of the tube) inside the artery. A cut might be made in the groyne to insert the stent. The balloon is made to inflate and deflate to open blockages and allow blood circulation to restore.

-
After the procedure
After the surgery, the hospital stay is usually 2-3 days. The full recovery takes about 6-8 weeks. You need to take care of the incision made during the surgery. Our doctor at Medanta will brief you about that. You will be advised to avoid strenuous activities and make healthy changes in your lifestyle.


The advantages of Peripheral Angioplasty treatment are:
- Improves artery blood flow.
- One does not need to undergo bypass surgery after this treatment.
- Relieves pain and heaviness in the leg.

The risks associated with the Peripheral Angioplasty surgery are:
- Allergic reaction to the drug used in a stent that releases medicine into the body.
- Allergic reaction to anaesthesia.
- Bleeding or clotting.
- Damage to the blood vessels and nerves.
- Damage to the artery in the groin.
- Stroke, heart attack, and kidney failure.
- Infection in the surgical cut.
- Misplacement of the stent.

This procedure does not have any major limitation, but sometimes the patient may require a subsequent open heart surgery or even amputation.